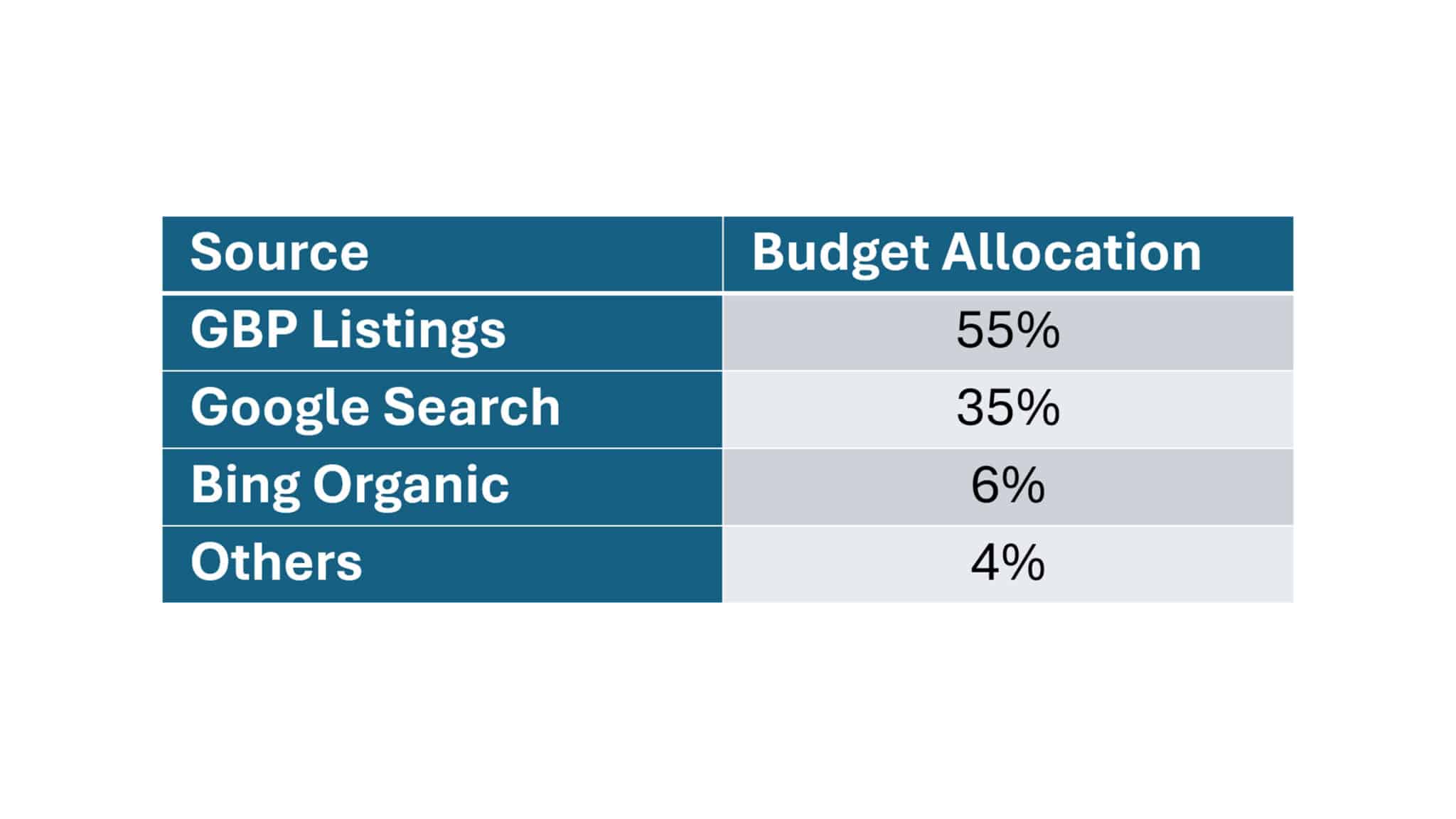
Google and Bing get a lot of attention, which you’d expect given both hold approximately 95% of the global search market share.
However, users searching for “Google alternatives” has increased by 7% year-on-year (mainly driven by a big spike at the end of May), with the U.S. seeing a 4% increase, according to data from Glimpse.
While this isn’t substantial, the spike at the end of May correlates with the period immediately after Google I/O and the less-than-desirable AI Overview results.
It’s uncertain how much the end-of-May spike was due to SEO articles about Google alternatives.
If broader market trends mostly caused the spike, the recent DOJ lawsuit might change how we understand the market’s reaction to Google and its feature issues.
It also reminds us that Google and Microsoft Bing aren’t the only search engines out there; they aren’t the only search engines developing core search products or new products and features using AI and LLMs as a backbone.
For several years, I’ve been covering Yandex, Baidu and other search engines worldwide as they develop their search products with and without AI.
Baidu (China)
Baidu has faced new competition in recent years. While it remains the dominant search engine in China, it has lost market share to non-traditional “search engine” applications.
Baidu is looking to AI to revamp its content ecosystem, bringing new capabilities to existing platforms like Baidu App, Baidu Content Ecosystem, Baidu Tieba and Baidu Marketing.
At the forefront of Baidu’s search revolution is Wenxin Yiyan (a.k.a. ERNIE).
ERNIE (Enhanced Representation through kNowledge Integration) is an AI language model developed by Baidu that leverages knowledge graphs to enhance natural language understanding and generation.
While ERNIE is a part of Baidu’s broader AI strategy, including applications in search, autonomous driving and cloud computing, in May 2024, Baidu disclosed that around 11% of traditional core search results were generated using AI technology.
Another key product in Baidu’s portfolio is Wenku.
Wenku is being transformed into a smarter, more intuitive document creation tool, much like Copilot, making it easier for users to create and manage content.
Baidu is, however, feeling the pressure as other platforms improve and work to acquire user focus, develop their own search tools and use AI.
Recently, competition has heated up even more. On July 10, Alibaba’s search engine, Quark, launched its AI-driven “Super Search Box.”
Tencent’s Yuanbao rolled out a new deep search feature on July 1, and DingTalk’s AI search started its exclusive testing phase on June 26.
Dig deeper: International SEO: How to avoid common translation and localization pitfalls
Yandex (Russia)
Yandex has claimed to have used AI in search technologies for more than 2020 years. At the 2020 YAC (Yet Another Conference), Tigran Khudaverdyan unveiled YATI (Yet Another Transformer with Improvements).
YATI is a machine learning algorithm developed to enhance its search engine capabilities. It focuses on better understanding the semantic meaning of search queries and documents, similar to human comprehension.
YATI processes more of the text content on a page than previous Yandex algorithms, which only looked at partial text on a page.
Yandex introduced Neuro, an AI tool designed for the Russian market and language, in May. It uses advanced linguistic models to handle Cyrillic script better than competitors like Gemini and Copilot.
Neuro is now integrated into important Yandex products, including Alice and YaBrowser. Its core functions and use are in image and speech recognition and NLP tasks like search and content creation.
Yandex upgraded its YandexGPT to the third version in April. At the time of launch, YandexGPT 3 was free (100 API requests per hour), and plans were made to integrate this technology into wider products.
Naver (South Korea)
A core element of Naver’s strategy is the introduction of “Cue:,” a new AI-powered search service designed to understand complex queries and provide structured conversational results.
After experimenting with Cue:, I’d compare it more to Copilot than to Gemini.
South Korean media have likened the extended use of Cue: to be closer to a search “personal assistant” than a traditional information retrieval search engine.
Cue: also appears to be positioned as an “add-on” to the traditional Naver search ecosystem and not detract from traditional results, Cafes or Blogs.
Cue:’s capabilities and success are down to the LLM behind it, HyperCLOVA X.
HyperCLOVA X builds on the original HyperCLOVA, first launched in 2021. The X iteration is more powerful, enabling complex, context-aware interactions beyond simple queries and has been integrated into other business tools, such as CLOVA studio.
Daum and NATE
Staying in South Korea, I feel it is important to mention two other region-specific search engines:
- Daum, operated by Kakao, uses AI to improve the relevance and personalization of search results. It tailors outcomes based on user behavior, particularly in news and local searches.
- NATE, by SK Communications, uses AI to enhance search accuracy, especially in news and life searches, focusing on trustworthiness. Its AI approach is more cautious, avoiding experimental or generative AI features.
Neither Daum nor NATE’s AI integrations are as prominent as Naver’s AI efforts, although according to a 2024 survey, Daum does have a higher market share in South Korea than ChatGPT.
Dig deeper: Multinational SEO vs. multilingual SEO: What’s the difference?
Seznam (Czechia)
Seznam.cz is a Czech search engine and web portal, often considered the “Google of the Czech Republic.”
In addition to its search engine, Seznam provides various other services like Sreality (real estate), Sauto (automobile classifieds) and Novinky (news).
Seznam’s LLM is already being utilized in its search engine, Vyhledávání, with plans to expand its deployment across other Seznam services this year and the next.
In June 2023, Seznam introduced Hacsiko, the first AI-created female presenter with a synthetic voice, on Expres FM radio. This marked a groundbreaking event in the audio market in the Czech Republic and Europe.
Seznam has also collaborated with Microsoft to showcase the practical uses of AI to Czech companies, showcasing them through the Seznam Native project.
from Search Engine Land https://ift.tt/bW48vLs
via
IFTTT